Comprehensive Guide to Business Insurance Cost in 2026
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Takeaways
- How much business insurance will cost in 2026 depends on the kind of business, the number of employees, the location, and the risk profile.
- The cost of public liability insurance, as well as other premiums, is affected by claims history, coverage limits, and industry risk levels.
- The contract terms and the insurance quote should be carefully reviewed to understand the available coverages.
- The data provided here is generic and doesn’t account for the individual situations of the businesses.
Knowing what affects business insurance costs in 2026 is not as simple as looking at a pricing guide. Insurance prices depend on factors such as the nature and location of the business, and the types of risks the company may be exposed to over time. Instead of providing set prices or suggestions, this article examines the typical ways insurance costs are determined in Australia and what business owners typically consider when their insurance cover is due for review.
This information is of a general nature and does not take into consideration your personal situation. It should not be regarded as financial, legal, or insurance advice.
This article provides general information only and does not take into account your objectives, financial situation, or needs.
Key Factors That Affect Business Insurance Cost
A single pricing rule does not determine business insurance cost. It is a result of various interconnected factors. In general, insurance companies evaluate business operational, financial, and risk-related information to determine insurance premiums that reflect the business’s total exposure.
Understanding these factors may help businesses better understand insurance offers and policy formats.
Understand the basics
It is always a good idea to get a grasp of the general concept of business insurance evaluation before one can name the exact cost factors. Insurance pricing reflects the probability of claims and the financial impact if a claim occurs during the business’s everyday operations.
Expenses are mostly figured out on an annual basis and may differ even for businesses in the same sector.
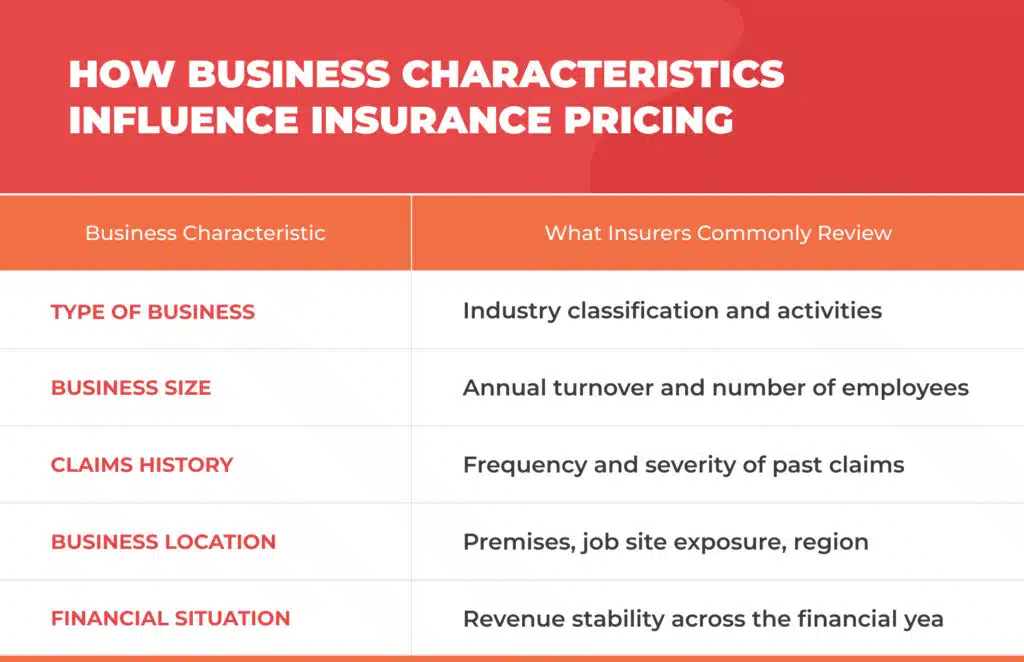
Type of business and business activities
One of the significant factors influencing business insurance costs is the type of business. Various industries have different levels of risk, especially if they involve physical work, interaction with the public, or specialised services.
Insurers analyse business operations to anticipate risks arising from routine activities. For instance, companies that work on job sites or come into contact with the public may face different liability risks than office-based professional services.
Business size, annual turnover, and number of employees
The size of an enterprise is most often determined by its annual turnover, annual revenue, and number of employees. These metrics help insurers estimate the potential size of claims and financial losses.
An individual self-employed person might have different insurance cost factors than a larger company with several employees, business premises, or commercial vehicles.
Claims history and risk profile
Insurance providers usually review a company’s claims history as the first step in understanding its past insurance experience. Such records help build the overall risk profile, which insurers use to evaluate future risk levels.
Fewer claims usually result in the business being considered a lower risk; on the other hand, more frequent or substantial claims affect insurance rates and base premium calculations.
Business location, premises, and job site
A business’s location is considered when determining insurance costs because different areas pose different risks, such as weather conditions, climate, crime rates, and the frequency of insurance claims. Besides that, the type of business premises and the job site may also be factored into the risk assessment.
Location-related issues can also differ across states like New South Wales and South Australia, which in turn determines how insurers gauge the risk of exposure.
Financial situation and financial year considerations
The financial position of a business can come under scrutiny, especially if the insurance coverage is related to sales or turnover. Broadly speaking, changes over a financial year, for example, business expansion or restructuring, may be reflected in premium adjustments at renewal, subject to insurer assessment and policy terms.
How Risk Impacts Insurance Premiums
Risk assessment is vital to calculate insurance premiums. Generally, insurers determine the likelihood of certain events and the potential financial consequences if they occur.
Higher Risk Versus Lower Risk Industries
Specific industries are mostly labelled as high-risk, whereas others are kept in the lower-risk category. Such classification is primarily based on past claims data, injury rates, and types of business operations.
Segments that involve physical labour or customer-facing work might be charged more for insurance than those with little or no physical interaction or operational hazards.
Result of Your Business Activities on Liability Risks
Usually, liability risks depend on the effects of business activities. Insurance providers evaluate the ways your business could impact third parties, their property, or the public in general during your everyday business activities.
A company that frequently comes into contact with third parties or their property will face greater exposure to liability claims.
Member of the Public and Injury Claims
Companies that have face-to-face dealings with the public may be vulnerable to injury claims, including personal injuries, medical expenses, and legal costs. These possible outcomes are taken into account when pricing liability-related cover.
Types of Cover and Their Costs for Businesses
Different types of cover address different risk areas. Each cover type is assessed independently, with premiums influenced by coverage limits, exposure levels, and business characteristics.
Common Insurance Covers
Public Liability Insurance Cost and Coverage: Public liability insurance is often viewed as a necessary liability of businesses that have contact with customers, suppliers, or the public. Public liability insurance costs depend on factors such as the nature of business activities, claims history, and the amount of coverage chosen.
Usually, this type of insurance protects against third-party property damage or personal injury claims arising from the firm’s operations.
Professional Liability Insurance for Professional Services: Any company that offers consulting or specialised services is likely to have professional liability insurance. Pricing is often associated with income level, contractual requirements, and the type of services provided.
Workers’ Compensation Insurance: Workers’ compensation insurance is a mandatory requirement for any business with a workforce. The cost is calculated based on payroll size, industry classification, and the number of workplace injury claims.
Business Interruption Insurance: Provides protection when the insured business experiences a loss of income due to the disruption of normal operations caused by insured events. The cost of the policy generally depends on a company’s turnover, its reliance on physical premises, and the indemnity period selected.
Cyber Liability Insurance: Cyber insurance and cyber liability insurance are attracting more attention nowadays due to increased digital exposure. Pricing of a policy is largely dependent on data usage habits, the strength of system security, and the amount of reliance on online operations.
Commercial Property Insurance and Landlord Insurance: Commercial property insurance and Landlord Insurance apply to businesses that either own or lease property. The value of the property, the type of building, business contents, and location-related risks can affect the premium amount.
Additional Insurance Options
Apart from the main covers, some companies decide to get extra policies depending on their business, properties, etc.
Car Insurance and Commercial Vehicles: Companies that operate vehicles as part of their work may need commercial car insurance. Premiums depend on the type of vehicle, how it’s used, and its claim history.
Equipment Insurance and Business Contents: Insurance for equipment and business contents may be of interest when the business uses tools, machinery, or portable assets that are essential to its operations. The item’s value and whether it is portable can influence the charges.
Home Insurance for Sole Traders: Several sole traders work from their homes. In those instances, home insurance policies should be carefully reviewed to determine which business-related risks are covered.
Tax Audit Cover and Medical Expenses: Tax audit cover may be offered as an option within a Business Insurance Pack. Some insurance policies may even cover medical expenses; however, this is always subject to policy wording and exclusions.
How to Get Accurate Business Insurance Quotes
Getting insurance quotes is not just about looking for the cheapest price. A clear understanding of how insurance policies are constructed may help businesses make better comparisons.
Steps for Comparing Insurance Solutions
- Most businesses identify their insurance needs by considering the types of operations they engage in, their assets, and regulatory obligations.
- Different types of businesses often have other insurance needs. An evaluation of the type of insurance commonly associated with business activities may help filter the options.
- When requesting insurance quotes, including Instant Quotes if available, policy documentation, such as the Product Disclosure Statement, should be carefully reviewed to understand conditions, exclusions, and coverage limits.
- Insurance brokers may provide general explanations of available cover options and clarify how different insurance solutions are commonly structured. Soliciting professional advice may be the right choice when insurance needs are complicated.
Cost Considerations for Small Business Owners
Insurance premiums don’t stay the same and may fluctuate when the business changes. Some small business owners periodically review their insurance policies to ensure they continue to reflect operational changes.
Typical things to think about include combining policies into a Business Insurance Pack, checking coverage limits, monitoring the claims history, and modifying the cover in line with business turnover or changes in operations.
Why VIM Cover Is Your Trusted Insurance Broker
Being clear about what an insurance broker does is one of the ways businesses can more effectively navigate insurance structures.
An insurance broker is generally someone who communicates between businesses and the insurance companies. They can help businesses by clarifying policy structures and coverage options and answering general insurance queries.
VIM Cover is an insurance broker that gives you access to a range of insurance options. Whether cover is offered, on what terms, and at what price is determined by the insurer, subject to underwriting assessment and policy conditions.
Insurance solutions are structured to suit businesses of different sizes, sectors, and operational models. The coverage a business receives can depend on the type of operations it conducts, its location, and the level of risk it faces. There is also support for companies that are extending their operations to other states, such as New South Wales and South Australia.
If you are seeking general information about business insurance structures or would like to view insurer-issued quotes, VIM Cover provides access to policy information and, where possible, Instant or Same Day Quotes. Any insurance decision should be made after reviewing the relevant Product Disclosure Statement and considering your own circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is business insurance cost calculated?
Insurers usually consider the type of business, turnover, claims history, number of employees, and the business’s operational risks.
Q2. Does a sole trader usually pay less for insurance?
A sole trader might enjoy reduced premiums if their operations are small, but the expenses still depend on the type of business activities and risk exposure.
Q3. Is public liability insurance mandatory?
Not all businesses are required by law to have public liability insurance. However, there are cases where one must be insured due to contractual or industry requirements.
Q4. Can insurance premiums change each year?
Indeed, rates can go up and down depending on a variety of factors, including claims history, business growth, changes to the level of cover, or insurer pricing reviews.